Shoulder pain can occur gradually and significantly reduce a patient’s quality of life. To find out why your shoulder hurts, you need to see a doctor and have a full examination. The most common cause of such pain is osteoarthritis of the shoulder.
The disease requires long-term appropriate treatment, which should only be prescribed by an experienced professional.
Which?
Shoulder arthrosis is a long-term, progressively progressive metabolic-dystrophic disease that leads to the gradual destruction of articular cartilage, a protective increase in bone tissue, joint deformity, and loss of function.
A wide range of arm movements is provided by the synchronous interaction of the joints of the shoulder complex:
- humeroscapular or simply humerus;
- acromioclavicularis - between the clavicle of the clavicle and the scapula;
- sternoclavicularis - between the sternum and the collarbone.
The shoulder joint is very mobile due to the convex head of the humerus and the relatively flat joint cavity of the scapula. The joint is strengthened by the tendons of the muscles of the upper limb, above which is the coracoid-acromial ligament. Unreliable reinforcement allows the joint to move in different directions, while increasing the risk of injury.
The code for arthrosis of the shoulder joint is M19 (other types of arthrosis) according to the International Classification of Diseases (ICD-10). Treatment of shoulder arthrosis should be started as early as possible. But even advanced stages of the disease can be successfully treated.
Causes of shoulder osteoarthritis
The main causes of arthrosis of the shoulder joint are:
- consequences of acute injuries - dislocations, subluxations, intra-articular fractures, bruises;
- long-term, long-term microtrauma related to the profession or sports exposure;
- transmitted acute and chronic infectious-inflammatory and autoimmune processes in the shoulder joint - acute purulent arthritis, chronic rheumatoid, psoriatic and other arthritis;
- in the background of the chronic inflammatory process of the periarticular tissues - humeroscapular periarthritis, which leads to damage to the blood circulation and nutrition of the cartilage tissue;
- metabolic (replacement) joint disorders - gouty arthritis;
- hormonal disorders;
- congenital disorders (dysplasia) - such as the joint surfaces of the shoulder joints.
Any of these causes (sometimes more than one at a time) will damage the composition and volume of the synovial fluid that feeds the cartilage tissue of the joint. The volume of cartilage gradually decreases, ruptures, and loses its padding properties. This leads to bone damage, growth along the edges of the joint surfaces, deformity of the joints, and decreased function. Inflammation of the synovial membrane in the joint cavity occurs intermittently - synovitis. Because of synovitis, arthrosis is called osteoarthritis or osteoarthritis, depending on which process is involved (inflammatory or metabolic-dystrophic). Inflammation and necrosis of the bone cause small pieces of tissue to separate from it - sequesters or joint mice.
Endangered:
- in case of microtrauma - blacksmiths, miners, tennis players, weightlifters, disc jockeys;
- in case of acute injuries - gymnasts, athletes, circus performers;
- persons with an inherited burden;
- persons with any chronic joint disease.
Symptoms of shoulder osteoarthritis
The disease begins gradually, gradually. The rate of progression depends on the cause, the general condition of the patient and the inheritance.
First signs
The initial symptoms of arthrosis of the shoulder joint may not be noticeable, especially if they are due to an existing shoulder disease. These are smaller, they occur intermittently, especially after exercise, pain, discomfort during joint movement. Left joint pain can be confused with heartache. They pass quickly, but they are worth paying attention to.
If such symptoms recur, it is better to see a doctor immediately because all diseases are easier to treat in the early stages.
Obvious symptoms
The pain increases and does not go away immediately after exercise. Nocturnal pains occur as well as pains associated with changes in the weather. The movements of the hand become painful, accompanied by a characteristic crackling. In the morning or if you stay in a certain position for a long time, the rigidity of the movements appears, you have to move to remove it. Pain syndrome can be localized not only in the shoulder area but also in the arms, neck and upper back.
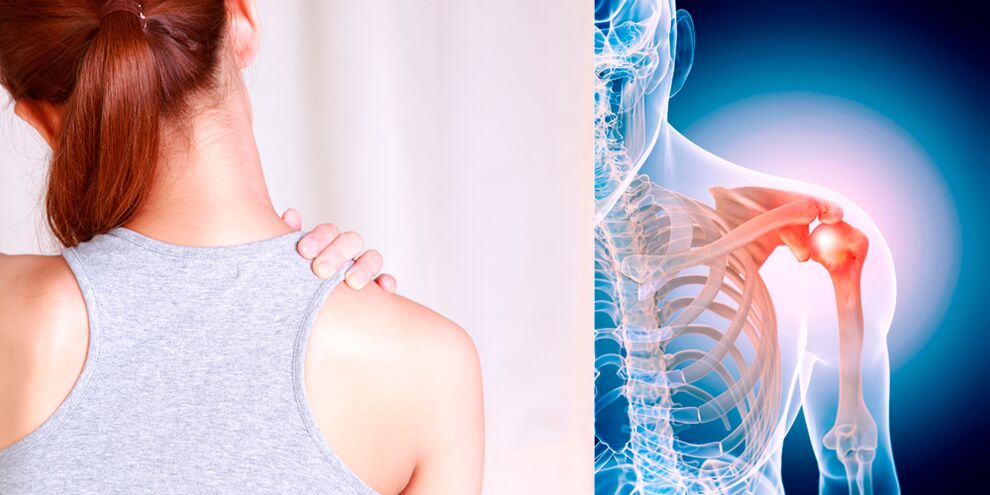
Sometimes the joint swells, a slight redness appears on it, the pain intensifies and becomes permanent. Body temperature may rise slightly. This is a sign of synovitis - aseptic (infection-free) inflammation of the joint membrane. If there are foci of infection in the body (carious teeth, otolaryngology, etc. ), it can enter the joint through the blood and lymphatics, causing a purulent inflammatory process. In this case, high fever and headache may occur, and the general condition may be severely disturbed.
The combination of degenerative-dystrophic and inflammatory processes in the joint gradually leads to permanent loss of limb function and permanent pain.
But even such patients can be helped, you just have to go to the clinic.
Dangerous symptoms
There are a number of symptoms of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint, indicating that you need urgent medical attention. This:
- edema and redness of the tissues in the joint area, fever;
- aching pain in the joint accompanied by deformation;
- joint pain radiates to the arm, neck, or back;
- the previous volume of movement in the arm is impossible, even lifting it causes severe pain.
These symptoms indicate that the body needs help. Only a doctor can provide it.
What is the risk of shoulder inflammation
In the absence of medical care, with the continuous progression of brachial arthrosis, it is a dangerous, persistent pain syndrome with decreased limb function and various, sometimes life-threatening complications.
Degrees of arthrosis of the shoulder joint
There are three stages of shoulder arthrosis:
- Arthrosis of the shoulder joint is 1 degreeinitial stage. All symptoms occur mildly and mostly after exercise. Mild narrowing of the joint gap is sometimes seen on X-rays, but not more often. At this stage, only magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can detect minor damage to cartilage tissue.
- Arthrosis of the shoulder joint is 2 degrees- progressive stage. The shoulder is constantly sore, the pain is intensified by the movement of the arm, lowered (on the elbow, forearm, hand) or on the neck, back, under the shoulder blade. There are difficulties in limb function, with periodic signs of synovitis. On X-ray, the joint space is significantly narrowed, bone growths (osteophytes) are seen at the edges of the joint surfaces, and bone tissue is condensed (osteosclerosis).
- Arthrosis of the shoulder joint is 3 degreesadvanced stage. The joint pain is strong, with a constant crackling when the arm is moved. The range of motion is limited, sometimes the arm is completely immobile due to pain. The joint is deformed, which sometimes leads to pinching of the nerves and blood vessels. On X-ray: the joint gap is almost invisible, significant bone growths with joint deformity, severe sclerosis and bone tissue death, joint mice.
Possible complications
Any localization and form of arthrosis has serious complications, so you should not delay treatment.
If you do not treat the disease or do not treat yourself with folk remedies, there is a risk of complications, such as:
- significant deformity and restriction of joint mobility;
- dislocations, subluxations, and intraarticular fractures with minor injuries or sudden movements;
- rupture of the tendons surrounding the joints of the muscles and ligaments - they atrophy and break easily;
- aseptic necrosis of the humerus head with complete destruction of articulation and loss of function;
- purulent-septic complications when the infection enters the joint cavity from other foci.
What to do with exacerbation
Exacerbation of the pathological process is usually associated with increased limb strain or the development of inflammation - synovitis. In this case, the joint hurts more, there is a slight swelling, and the body temperature rises. In such cases, you should follow the following self-help algorithm:
- call a doctor at home;
- take one tablet of one of the painkillers;
- apply anesthetic ointment to the skin in the area of the patient's joint;
- tie the sore arm with a bandage - this reduces the load;
- take an elevated posture - sit down with a pillow under your back - this will reduce tissue swelling.
Types of shoulder joint arthrosis
According to different criteria, the disease is divided into separate types.
Due to illness
According to this criterion, a distinction is made between primary and secondary osteoarthritis. Primary shoulder inflammation is primarily the result of age-related changes and develops after 50 years. But sometimes the disease begins at a young age, but the cause cannot be determined. In this case, they talk about primary idiopathic arthrosis of the shoulder. Hereditary predisposition plays an important role in its development: the presence of a similar disease in one of its close relatives.
Secondary arthrosis of the shoulder joint develops after injuries and previous illnesses, but here too, inherited matter matters: in one person, even a minor injury or acute arthritis can lead to arthrosis, while in others the more significant damage ends without consequences.
According to the flow characteristics
Designation of deforming arthrosis of the shoulder characterized by rapid progression of bone deformities. One of the features of this type of disease is a change in the shape of the joint and frequent damage to nearby blood vessels and nerves. Compression of blood vessels impairs blood circulation and the rapid progression of degenerative-dystrophic disorders, and compression of nerves leads to impaired limb sensitivity and severe pain along the peripheral nerves.
Origin
Post-traumatic arthrosis of the shoulder - the symptoms and treatment of the disease have their own characteristics, which are associated with traumatic changes in certain joint structures. Exchange dystrophic lesions occur after intra-articular fractures, dislocations, subluxations, ligaments, tendon ruptures, and simple bruising. Injuries result from a blow to the joint or a fall to the side if the arm is contracted. Displacement cracking of the joint sheath usually occurs during a fall on the abducted arm.
Often, after a minor injury, a person does not notice the first signs of arthrosis for a long time and seeks medical help as early as the second stage of the disease. Significant injuries require long-term rehabilitation treatment, and arthrosis is usually treated at an early stage.
Shoulder joint arthrosis after inflammatory diseases - the symptoms and course of such pathology depend on the underlying disease. The shoulder joint is often affected in psoriatic arthritis, while arthrosis develops in a joint, develops slowly but is difficult to treat. In rheumatoid arthritis, both shoulders are affected, arthrosis develops in waves, with frequent alternation of metabolic-dystrophic and inflammatory processes.
dissemination
It can only affect one left or right joint and then they talk about monoarthrosis. The simultaneous defeat of the two (left and right) shoulder-shoulder joints is called oligoarthrosis.
Arthrosis of other joints of the shoulder complex
Acromioclavicular arthrosis - most often of post-traumatic origin. It is formed in the background of lifting weights by hand above the horizontal. It is accompanied by pain when the arm is lifted. As osteophytes grow on joint surfaces, impingement syndrome can occur - damage to the shoulder tendons and muscles between the humerus head and the scapula acromion during shoulder rotation and abduction. This accelerates the progression of arthrosis and the decrease in hand function.
Diagnostics
Without a correct diagnosis, it is impossible to treat this disease. A full examination is only possible at the clinic. During the first consultation, the doctor asks the patient, examines it, prescribes further research methods and specialist consultations:
- Laboratory tests of blood, synovial fluid - inflammatory, autoimmune and degenerative-dystrophic processes can be detected.
- Instrumental:
- radiography of the shoulder joint - changes in bone tissue are detected;
- computed tomography (CT) - changes in cartilage and bone tissue in the early stages;
- magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) - changes in soft joint and periarticular tissues;
- diagnostic arthroscopy - if necessary to clarify the nature of the pathological process.
Treatment of osteoarthritis of the shoulder joint
Once the final diagnosis is made, complex conservative treatment of shoulder arthrosis is prescribed. If conservative therapy is ineffective, surgical treatment is prescribed.
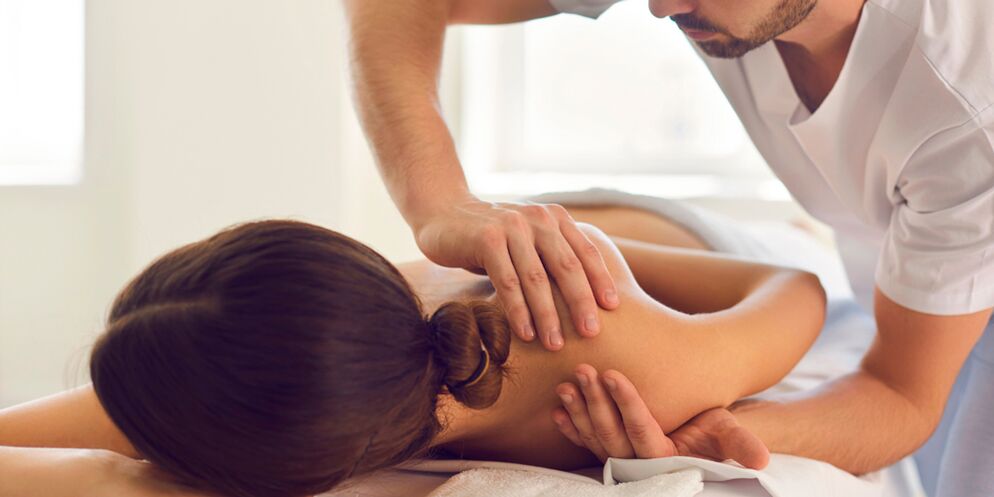

Conservative therapy
Contains pharmacological and non-pharmacological methods.
Medical treatment
The goal of medication is to relieve pain and reduce the progression of osteoarthritis. To alleviate the patient's condition, the following should be prescribed:
- Drugs from the groupnon-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). The drugs are administered intramuscularly, orally or rectally; however, drugs belonging to the NSAID group are prescribed externally in the form of ointments, gels, or creams.
- Drugs from the groupmuscle relaxants- relax the muscles surrounding the joint; the spasmodic condition of these muscles increases the pain;
- Pain blockadeswith local anesthetics.The drug solution is injected into the joint cavity or periarticular tissue - a quick analgesic effect.
Pathogenetic therapy (affecting the mechanisms of the disease) as part of the medical treatment of shoulder arthrosis includes:
- Chondroprotectors- medicines that contain biologically active substances that restore cartilage tissue. It is prescribed orally in the form of tablets and powders, intramuscular and intraarticular injections, and externally in the form of ointments and creams.
- Angioprotectors- Devices to improve blood microcirculation. In tablets and intravenous drip solutions for oral use.
- Hyaluronic acid preparations- are placed in the joint cavity to improve its cushioning properties and prevent the destruction of bone tissue.
Vitamin-mineral complexes to improve metabolic processes in joint and periarticular tissues.
Non-pharmacological treatment
Non-drug treatments for shoulder arthrosis are based on a healthy, active lifestyle and proper nutrition. It is very important to get rid of bad habits such as smoking and alcoholism - these contribute to circulatory disorders and have toxic effects on joint tissues.
Nutrition, diet
There is no special diet for the treatment of shoulder arthrosis, but proper nutrition is very important in this disease. It is recommended to include in the daily diet: sea fish, seafood, lean poultry, dairy products, cottage cheese, cheese, cereals (oatmeal, buckwheat), vegetables, fruits.
Excluded from the diet: easily digestible carbohydrates (sweets, muffins, sweet carbonated drinks), fatty red meats, tissue irritating foods that cause swelling - salt (in excess), spicy and spicy spices.
It is recommended to give preference to cooked, steamed and steamed foods.
Orthopedic treatment to distribute the load on the limb
To prevent shoulder injuries, it is recommended to wear an elastic protective fastener in the form of a short sleeve attached to the opposite arm from time to time. The device improves blood circulation and eliminates swelling. But wearing it permanently is not recommended as it leads to a rapid decrease in the range of motion of the shoulder.
Many professionals use banding in the complex treatment of shoulder arthrosis - securing tissues with sticky elastic bands. It eliminates pain, improves blood circulation and joint function.
Physiotherapy
Gymnastics - a daily series of exercises - is the main method of rehabilitation for shoulder arthrosis. Gymnastic complexes are prescribed by a doctor and mastered under the supervision of a gymnastics instructor. Once the patient begins to perform the full set of exercises correctly, it can be performed at home.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy is part of complex therapy at any stage of the disease. These are electro- and phonophoresis with analgesics, laser and magnetotherapy - stimulation of regenerative processes in joint tissues, shock wave therapy (SWT) - sound exposure, which has a pronounced chondroprotective effect.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies only have great benefits prescribed by a doctor. Here are some of them:
- Decoction of viburnum branches for oral use.Pour a glass of crushed raw material with 500 ml of water before going to bed, bring to a boil, keep on low heat for 5 minutes, insist overnight, then filter and drink 100 ml 3 times a day. This is an anesthetic.
- An old recipe for an anesthetic ointment from wild rosemary herb.Take Vaseline or butter and dry the cut grass. In an enameled dish, fold the grease base and grass alternately in layers, cover the pan, spread the cracks with dough and place in the oven (preferably in the oven) over low heat for 2 hours, remove from the oven, filter through double gauze and refrigeraterub the diseased joint into the skin 2-3 times a day.
Surgical operations
Due to the ineffectiveness of conservative therapy for arthrosis of the shoulder joint, the following surgical procedures are performed:
- Arthroscopic surgeriesallows you to eliminate various defects in the joint cavity. It is mainly performed in young people with post-traumatic arthrosis. Arthroscopy allows the biceps tendon to be tightened and attached to the bone (tenodesis - this eliminates loosening of the joint), removes bone growth - osteophytes (debridement), restores the joint cavity by transplantation, and so on.
- Endoprosthesis- replacement of a damaged joint that has lost its function with an artificial one.
Approach to treating the disease in clinics
Clinicians have developed their own approach to treating shoulder joint arthrosis. Above all, all patients are carefully examined with state-of-the-art diagnostic equipment (including MRI). It is then completely relieved of pain by pharmacological and non-medicinal methods. However, individual complex therapies are selected for him, including:
- state-of-the-art drugs and non-drug methods, including plasmolifting;
- restoring traditional oriental treatment methods and joints and the whole body; these are acupuncture, moxibustion, auriculotherapy, taping, etc.
This approach quickly relieves pain and suppresses disease progression. And regular prevention courses allow patients to forget about their illness and live a normal life. Several patient reviews talk about how effective this treatment is.
A combination of Eastern best practices and innovative methods of Western medicine.
General clinical guidelines
Recommended for people with shoulder inflammation:
- leading a healthy, agile lifestyle, alternating physical activity and rest;
- eat right regularly;
- get rid of all bad habits;
- perform therapeutic exercises regularly to avoid sudden movements;
- sleep at night on your back or on the healthy side and place a small pillow under the sore arm;
- stop strenuous physical exertion, avoid injuries, prolonged stress, and colds;
- avoid thermal procedures during exacerbation (development of synovitis);
- follow all the recommendations of your doctor.
Prevention
It is especially important for people with aggravated heredity to follow certain rules to prevent shoulder inflammation. Do not engage in weightlifting, tennis, traumatic sports, work as a hammer, blacksmith or miner. Everyone who wants healthy joints should lead an active lifestyle and eat regularly.
Frequently asked questions about the disease
- What pain does osteoarthritis cause in the shoulder?
The pains are painful, exacerbated by movements and weightlifting.
Why is the disease dangerous?
Development of persistent pain syndrome and loss of limb function.
Which doctor treats shoulder deformity arthrosis?
Post-traumatic - orthopedic traumatologist, in the background of inflammatory diseases - rheumatologist.
Is blockade of the shoulder arthrosis performed?
Yes, for severe pain.
How effective are physiotherapy methods for this disease?
Effective as part of a complex treatment.
Is It Possible To Completely Cure Shoulder Deforming Arthrosis?
No, but the doctor can suppress its progression and save the patient from the pain.
Shoulder arthrosis should be treated for a long time, systematically and strictly under medical supervision. Attempts to cope with the disease on their own are associated with complications and disability. But a trained professional can stop the process at any stage of the disease, save the patient from pain, and significantly improve their quality of life.

















































